New habitats for flora and fauna
In cities and municipalities, residential and commercial space is scarce. Through new buildings and densification, thousands of hectares of soil are „sealed“ every year. As a result, natural cycles are destroyed, since soil is the habitat and livelihood of humans, animals and plants. Soil is an integral component of water and nutrient cycles. It also fulfils important filter and buffer functions – especially with regard to groundwater. Planted roofs are an excellent way to replace at least partially the lost soil functions.
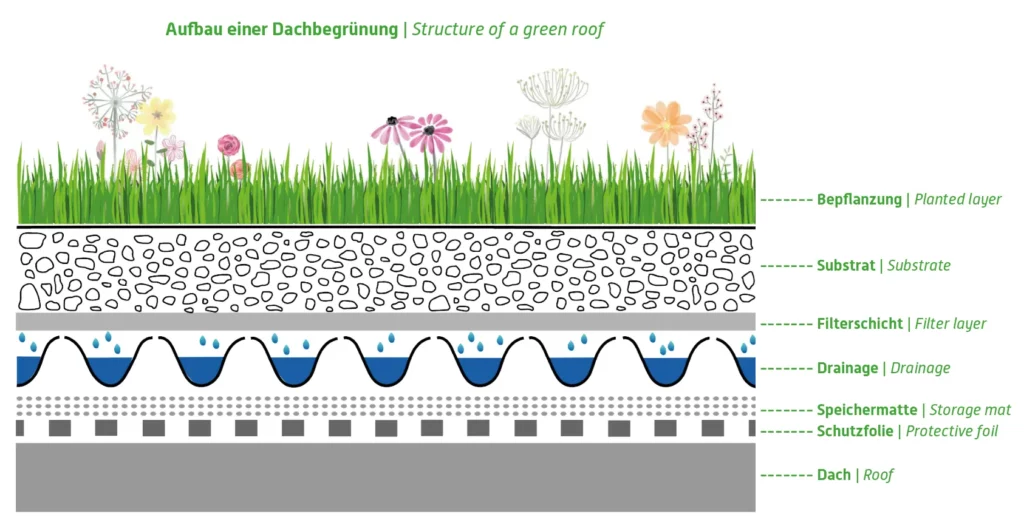
Urban climate
Gründächer produzieren Sauerstoff, binden Kohlendioxid und Feinstaub. Green roofs produce oxygen, absorb carbon dioxide and particulate. Through evaporation of rainwater, they also cool the buildings and their surroundings in summer.
Habitat
Green roofs provide an additional livelihood for bees, bumblebees, butterflies, beetles and birds.
Precipitation retention
Green roofs store rainwater and release it later in the form of evaporation. In this way, sewage systems are relieved during heavy rainfall events (reduction of peaks).
Living environment
Green roofs do not heat up so quickly in summer and have a cooling effect. In winter, the roof does not cool down as quickly and has a heat-insulating effect. In addition, the dense plant mat has a soundinsulating effect.
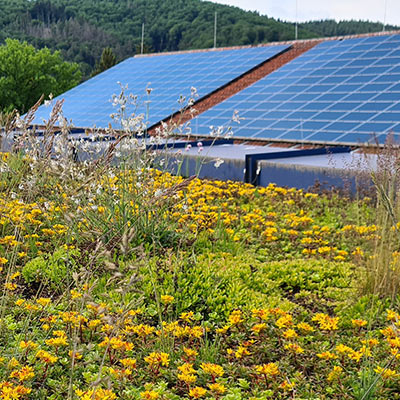

Making photovoltaic systems more efficient
Green roofs and photovoltaics are not mutually exclusive. On the contrary, the cooling eff ect of green roofs in summer has a proven positive impact on the performance of photovoltaic systems.
Green roofs
- promote biodiversity and a natural climate.
- reduce the need for heating in winter, have a cooling effect in summer like an air conditioner.
- prolong the life span of roofs (protection against UV radiation & weathering).
- can be installed on flat and pitched roofs.



