There is no waste in the forest ecosystem
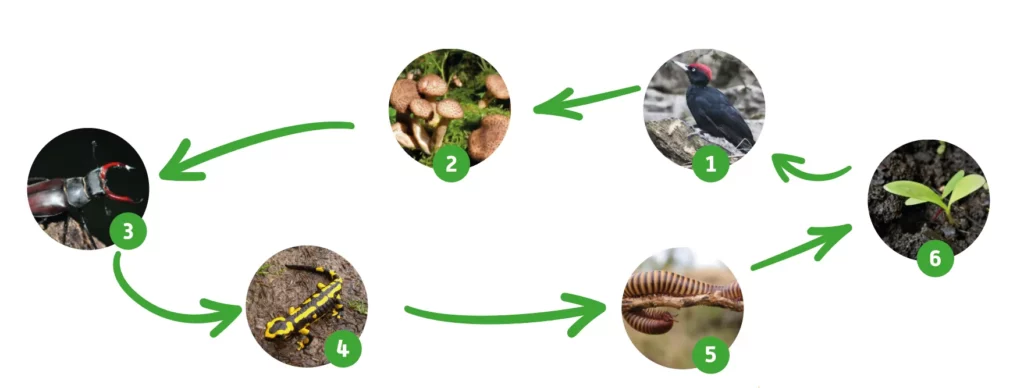
Everything is recycled. When wood dies, it becomes the basis for new life (deadwood). Countless organisms participate in the constant decomposition and regeneration.
About 20 percent of the forest flora and fauna live directly or indirectly from deadwood, including fungi, lichens, mosses, ferns, insects, reptiles, birds and also mammals, such as the cave-dwelling marten. Many of these are already threatened with extinction. The majority of our 1,000 species of wasps and bees depend on it. Many other insect species such as butterflies, beetles, ants, flies, crane flies, heteropterans, moths, arachnids and mites find their habitat here – use it as shelter, food source and building material.
The various interdependencies between fungi and insects give rise to biocoenoses. Insects transfer fungal spores to the wood body, the fungi in turn can be a food source and partial habitat for insects.
Old and dead wood
- fosters nature conservation and species protection.
- contributes significantly to natural disease and pest control in the forest.
- has a positive effect on the microclimate. Prevents the soil from drying out, can compensate temperature and humidity fluctuations.