Clever linking of climate protection and nature conservation
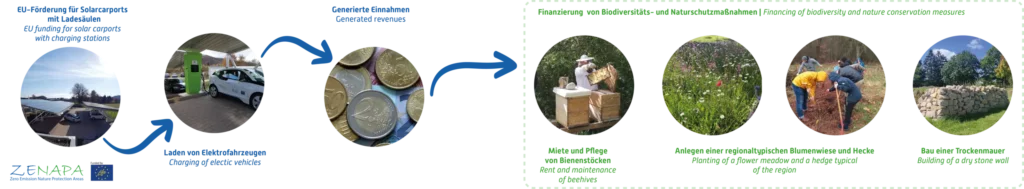
Through the example of the EU-funded photovoltaic carports with charging stations, the Environmental Campus shows how climate protection projects can also benefit nature conservation. Not only do climate-friendly technologies make sense from an ecological point of view, but are oft en also profitable. If the revenues generated by such projects are invested, at least in part, in regional environmental projects, the benefits are twofold: for the climate and for
biodiversity.
One practical example are the beehives on the campus grounds, whose rent and maintenance are financed by the revenues generated from charging electric vehicles at the installed charging stations. In addition, other projects, such as the construction of a dry stone wall and the planting of a perennial flowering meadow as well as a biodiverse hedge, were implemented using these proceeds. This sustainable concept creates regional value, as electricity is produced locally, revenue is retained locally, regional honey is produced and, at the same time, the concept also contributes to species conservation.
Bees & Co. – Why we need pollinators
Honey bees, wild bees, butterflies and many other insects play a central role in the pollination of a wide variety of cultivated and wild plants. It is estimated that they pollinate around 80% of our native flowering plants – and thus secure the livelihoods of humans and animals. However, these important pollinators are under threat in many places and, as a result, so are our natural food sources.
Pollinators
- are often endangered species, e.g. due to monocultures, pesticides, soil sealing and climate change.
- only have a limited food supply and few habitats left .
- by pollinating plants, they provide the basis for food for humans and animals.
- hey are important for maintaining the balance of the Earth‘s ecosystem.